Key Components of a Data Governance Framework

What is Data Framework?
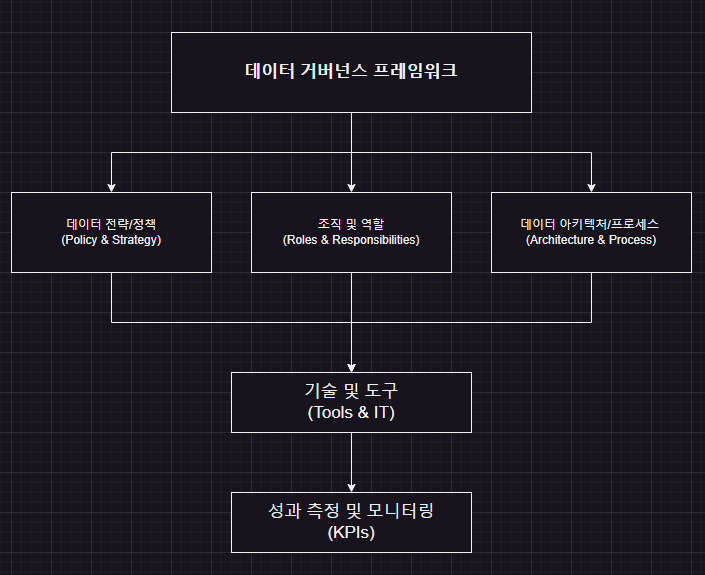
A data governance framework is composed of multiple interconnected elements that together form the overall data management system. It typically includes:
Data Strategy & Policies
Define the organization’s data utilization objectives, vision, and mission, and establish policies on data security, privacy, quality, and compliance.Organization Structure & Roles
Clarify the roles and responsibilities of data stakeholders—such as the Chief Data Officer (CDO), Data Steward, and Data Owner—to assign clear accountability for data management.Data Architecture & Processes
Design the end‑to‑end lifecycle of data—including ingestion, storage, integration, transformation (ETL), and analysis—mapping out each process step.Technologies & Tools
Build the technical infrastructure, including data repositories, ETL tools, metadata management systems, and data quality monitoring platforms.Metrics & Monitoring
Use KPIs, dashboards, and data quality indicators to assess the effectiveness of policies and processes and drive continuous improvement.Training & Communication
Establish education programs and internal communication channels so that all stakeholders understand and adhere to the framework and its policies.
2. How the Framework Operates
During the Plan phase, the data governance framework functions as follows:
Set Objectives & Establish Policies
Craft data management strategies and policies aligned with business goals—e.g., strengthening data security, improving quality, and enabling efficient data use.Assign Roles & Responsibilities
Delegate data‑related duties to departments and individuals, and specify the corresponding authority and accountability.Define Processes
Design detailed procedures for data collection, storage, processing, distribution, and disposal—incorporating validation and monitoring steps at each stage.Implement Technical Infrastructure
Select and deploy IT systems (databases, ETL platforms, metadata tools, etc.) that support the defined policies and processes.Monitor Performance & Feedback
Continuously evaluate data management outcomes against the established KPIs and dashboards, and refine policies or processes as needed.
By clarifying what will be managed, who is responsible, and how it will be done, the framework ensures that raw data is systematically cleansed, stored, and leveraged.
3. Considerations When Building the Framework
Alignment with Business Goals
The data governance framework must be fully aligned with the organization’s overall business strategy.Flexibility & Scalability
Start with a core structure, then adapt it flexibly as data volumes and complexity grow.Culture & Training
Foster a culture in which team members understand and comply with policies and procedures through ongoing education.Continuous Feedback
Regularly monitor and review the framework to validate its effectiveness and drive iterative improvements.
